Blind Signatures & Chaumian eCash
This guide has been developed as a community project and is a live document. We would appreciate any feedback you may have and you can submit edits, corrections and pull requests through the link at the bottom of each page.
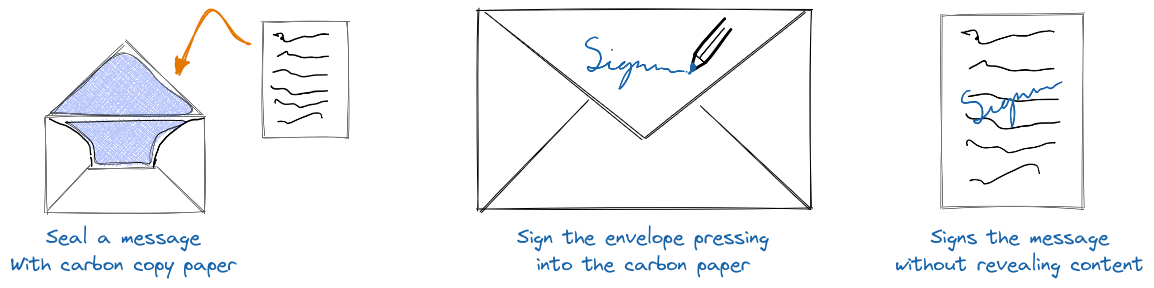
The canonical explanation of blind signatures was given by David Chaum in terms of imprinting a signature on a message using carbon copy paper.
As highlighted in the figure above, imagine obtaining a signature on a document as follows:
- Create a document and seal the document into an envelope along with carbon copy paper.
- You pass the envelope to the signer who can sign the outside of the envelope.
- This creates an internal signature onto the document from the carbon paper. .
- If you were to reveal your document at a later date, the signer could confirm that they did indeed sign that document.
This is the concept utilized inside eCash, allowing an eCash mint to issue "IOUs" that it can confirm are valid, whilst retaining the privacy of the user.
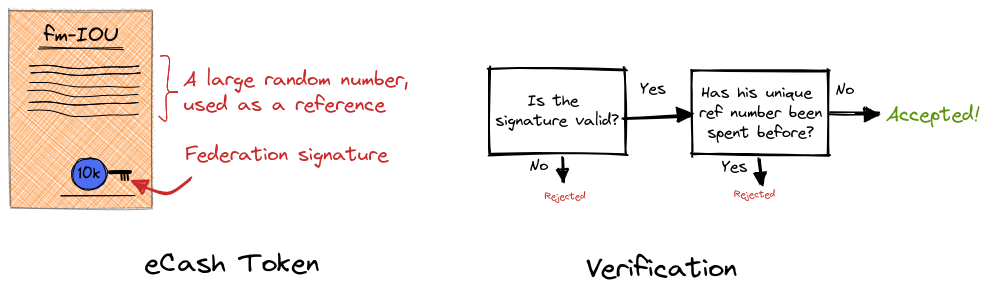
A user can present a mint with a random identifier and request a blind signature from the mint. The mint signs different denominations with different private keys (for example a 10k Sats private key, a 5k sats private key and so on).
So when a deposit (lets say 10,000 satoshis) is made, the user presents the mint with a random identifier and requests a blind signature with their 10,000 satoshi private key.
These two piece of data make up an eCash token.
When it comes time to redeem these satoshis, the user provides the mint with the eCash token and it performs two checks:
- The mint confirms the signature was made with their 10,000 satoshi private key.
- The mint checks it has not previously redeemed an eCash token with this unique reference number.
If both of these checks pass then the eCash token is accepted.
Until this redemption is made the mint is unaware of the unique reference number on the eCash token, as a blind signing algorithm was used.
This means that the mint is unable to ascertain the following information:
- Whether the individual redeeming the token was the same individual who minted the token.
- What the number of tokens held by any individual user are.
This is the basis of the strong privacy claims in eCash.