Core Technology Components
This guide has been developed as a community project and is a live document. We would appreciate any feedback you may have and you can submit edits, corrections and pull requests through the link at the bottom of each page. Let's build the future of Bitcoin custody together!
Fedimints use three powerful technical components, that come together to offer great privacy and interoperability:
- Chaumian eCash: Privacy preserving online digital cash, pioneered by David Chaum.
- Federations: Shared control of assets and system enabled by threshold signatures and consensus algorithms.
- Lightning swaps: economic transactions to swap a common asset between different layers.
All three technologies come together to allow users to delegate the complicated tasks of managing their bitcoin holdings and lightning nodes, whilst retaining financial privacy.
Chaumian eCash
Chaumian eCash allows the Fedimint to create and redeem IOU notes that represent claims on bitcoin.
The technology was originally developed in 1983 by David Chaum and realized through the company Digicash.
Digicash, allowed users to purchase $ denominated eCash bank notes, that could be transferred over the internet to perform payments, in effect creating the worlds first internet bank.
The process of issuing and redeeming eCash notes was made anonymous through the use of Blind Signatures.
This is covered in detail at Definitions and Terms > Blind Signatures & Chaumian eCash.
This process relied on a centralized server to confirm authenticity of certificates and eliminate double spend issues, however, the server had no knowledge who the eCash notes belonged to.
This allowed users to transact privately on the internet without the bank being aware of the specific transactions and payments made, or the balances held by any specific user.
This is very important in a community banking setting where knowing the exact balances of all the people in your local community could expose individuals to physical attacks if the information is leaked or hacked.
Federations
Fedimint is a "federated Chaumian Mint."
This means that the mint is jointly owned and operated by multiple people, we refer to as guardians.
This approach has been commercialized by Blockstream in the Liquid Bitcoin side chain.
By federating the operation, Fedimint gains several advantages over single server deployment.
- The bitcoin held in the mint is never subject to the control of a single individual making it harder for a corrupt guardian to steal funds.
- Increases redundancy as guardians can go offline and transactions will still be processed where a quorum is reached.
- Changes the regulatory space of the federation as no single individual controls coin issuance and redemption.
This replicates the best practice model of multi-signature custody, used in exchanges and custody providers globally.
Lightning Swaps
Integration with the lightning network is achieved using lightning swaps that are provided as a service to the users of the mint.
A simple way to think about this is by imagining a man with two bags. One bag is full of Fedimint bitcoin, one bag is full of Lightning bitcoin and he is willing to sell either for the other.
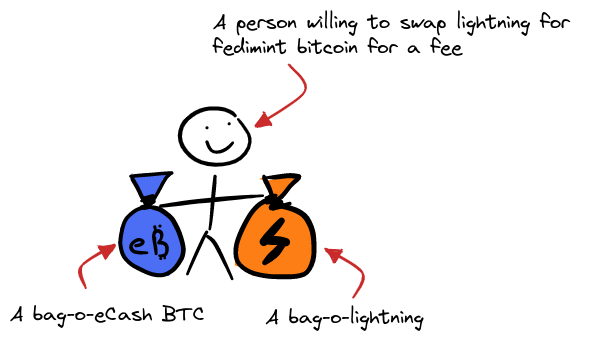
This is how lightning gateways work.
These users will accept Fedimint bitcoin to pay a lightning invoice on your behalf, or accept incoming lightning invoices and pay you in Fedimint bitcoin.
These payments are secured in both the Fedimint and the lightning network using a common Hash Time Lock Contract.
This in effect "extends" the lightning route 1 more hop into the federation and ties together the success of both payments.
Lightning bitcoin never "transforms" into Fedimint bitcoin, completing the swap is more like a balance sheet exercise for the lightning gateway operator.
It is also possible to run multiple lightning gateways on a Fedimint and for any users to become a lightning gateway as long as they run a lightning node.